After email verification, it’s time to review the results in your report.
When you upload a list for email verification on SafetyMails, you need to wait for some time until the report become available to you. This time is valuable and essential because our algorithms are dedicated to verifying all your emails with the utmost precision.
If you want direct access to an explanation of a specific part of your email verification report, use the index below:
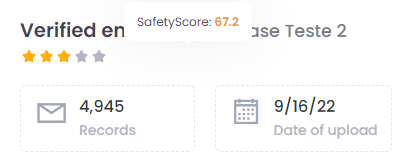
SafetyScore
SafetyScore is the quality score of an email list imported into the tool, based on the criteria adopted by SafetyMails.
This score primarily takes into account the incidence of invalid emails and spam traps, responsible for most blocks and drops in reputation in email marketing.
The higher the stars, the better the quality of the list imported into SafetyMails.
This score can be seen by hovering over the stars below the name of your database.
Email Statuses
After email verification, addresses are classified according to Safetymails’ criteria.
The distribution of these emails can be seen in a graph and also in a table, like this:
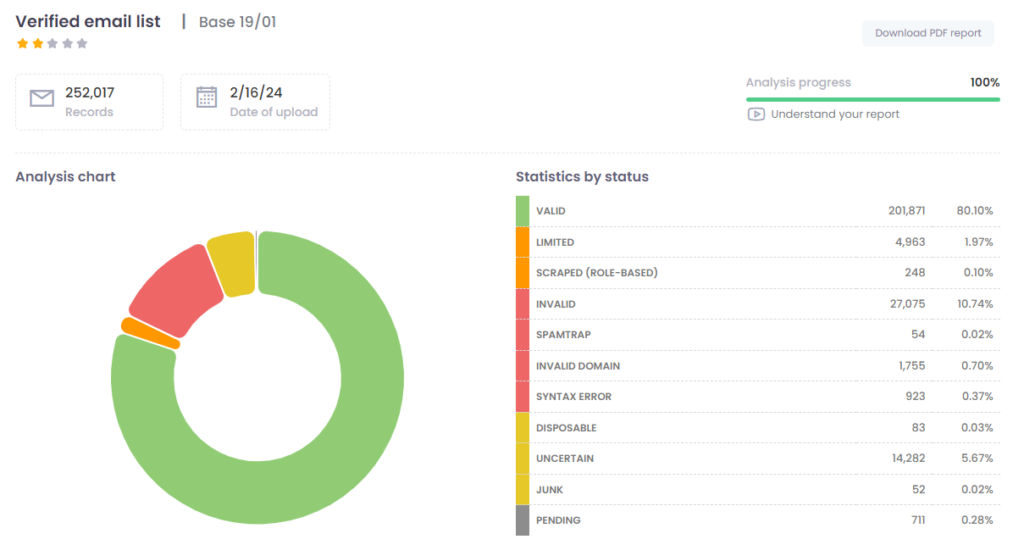
The table below explains the statuses presented:
GREEN zone
These email addresses can be used in your campaigns.
| Valid | email address whose existence has been confirmed. |
ORANGE zone
These email addresses can harm your campaigns due to their low deliverability.
| Limited | Valid Email Addresses that Knowingly Have Limitations on Receiving Capacity, Such as Intermittent Server Issues. This Can Lead to Delivery Problems. |
| Scraped | ISPs admit that these emails have been created by automatic generators of addresses such as “contact, adm, sales, etc” for various domains, characterizing spam by “Dictionary Harvest Attack”. They can also be emails from callcenters or others that do not have a responsible individual. |
RED zone
These email addresses MUST NOT be used in your campaigns.
| Invalid | E-mail classified as non-existent or deactivated in a domain. Hard bounce. |
| SpamTraps | Trap emails are used to capture spammers, causing immense damage to the reputation of IPs, leading to blocks and a decline in deliverability. They are not disclosed in the database to contribute to the fight against spam. |
| Invalid Domain | This email address is invalid because the domain does not exist, was mistyped, or is unable to receive emails due to its settings. Please do not send messages to this email address. |
| Syntax Error | E-mail that does not comply with the syntax rules set by email providers and market RFCs, since it invalidates the email. |
YELLOW zone
These email addresses have characteristics that make sending them UNRECOMMENDED. Therefore, it is up to the client to decide what to do, but they will be subject to problems with email providers.
| Disposable | E-mails from temporary address services. They are valid, but only for some time (hours or minutes). After this period they become invalid and impair deliverability. |
| Junk | E-mail addresses that have negative elements that will be identified by ISPs and sent to the junk folder or spam. E-mails with repeated characters, swear words, numeric sequences, etc. |
| Uncertain | Known as “Accept All” and “Deny All”. That is, they receive all messages or deny all messages, regardless of their content. The result cannot be confirmed. |
GRAY zone
These are e-mails for which we have no information and therefore no credits have been debited from the customer’s account. There is no validation response.
| Pending | Emails for Which We Currently Lack Information in Our Database. After a New, Specific Analysis Period for These Addresses, We May Still Lack All the Information. Credits for These Emails Are Refunded to Your Account. |
Distribution by error and by risk
These graphics seek to elucidate information regarding the emails that should not be used by the client, such as those with errors or some kind of risk.
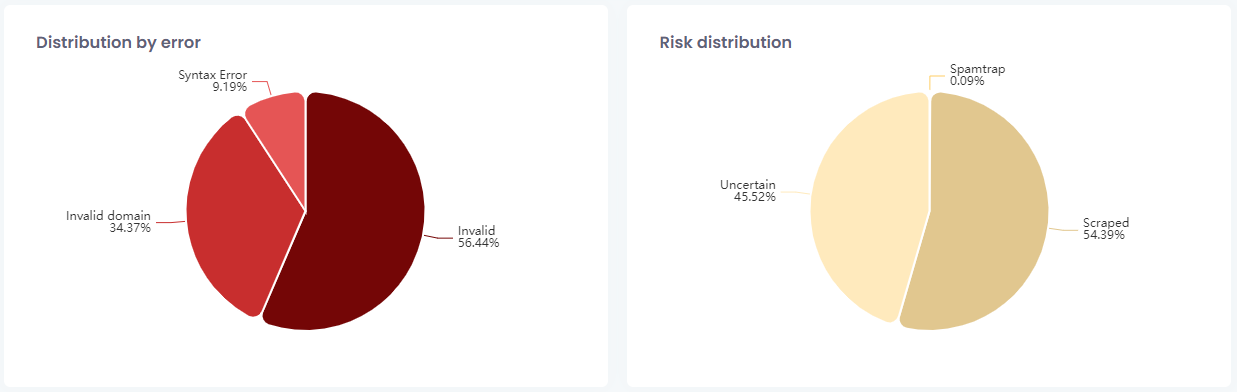
Distribution by risk
Indicates the distribution of emails with errors, broken down into invalid, syntax errors and invalid domain.
Distribution by risk
Indicate the distribution of emails that pose some kind of risk to the reputation of email marketing, such as disposable, junk, scraped, spamtrap, and uncertain emails.
Behavioral distributions
This area of the report is dedicated to delivering information from domain interpretation and email syntax, as shown below:
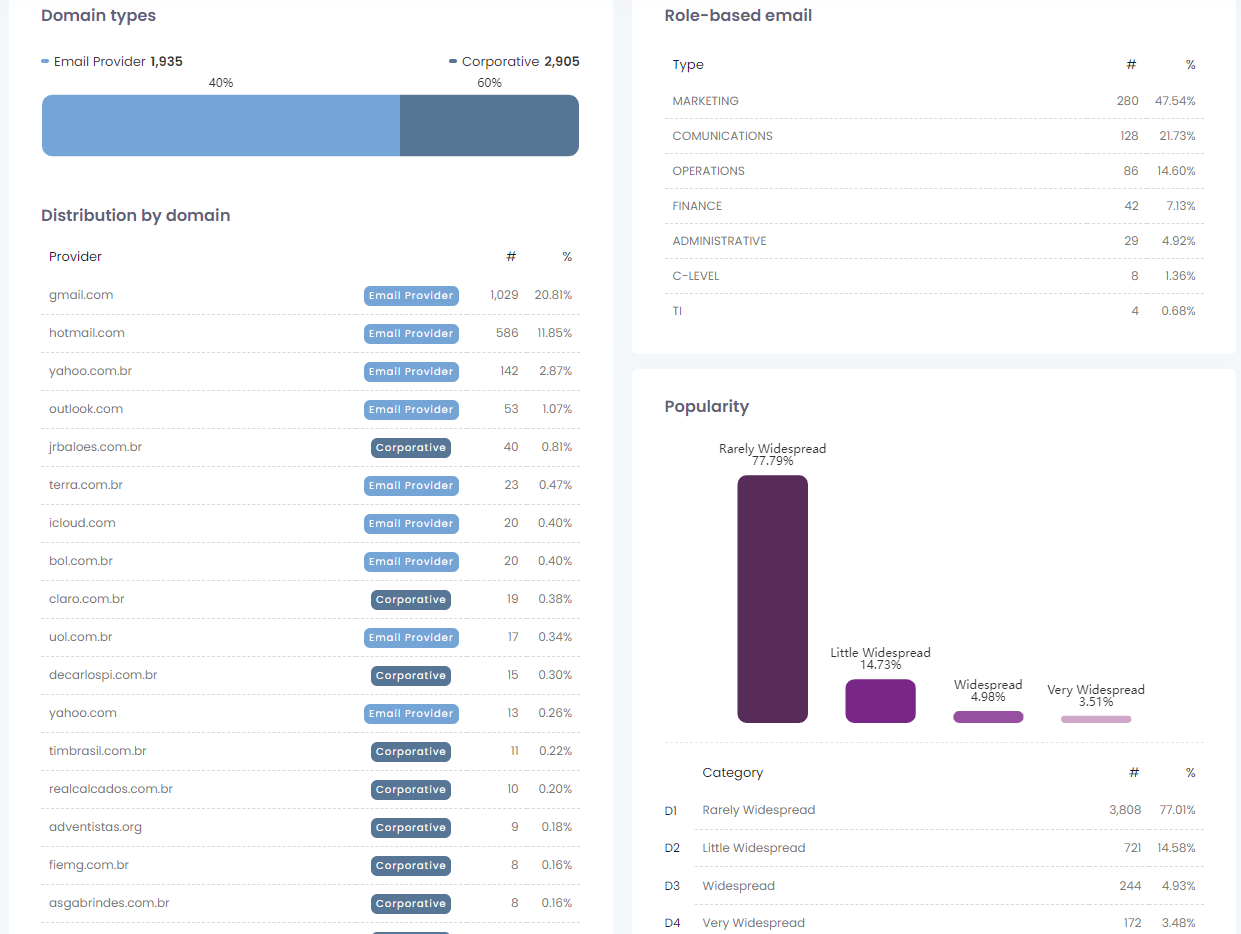
Types of domains
Here you will have a demonstration of how your base is formed, taking into consideration emails from providers (Email provider) or emails from companies (Corporative).
Distribution by domain
This report shows the percentage share of each provider (such as Gmail, Yahoo, etc) in your imported list. It also individually categorizes each provider according to domain type criteria (Email Provider or Corporate).
Role-based emails
SafetyMails tries to classify the e-mails identified as corporate according to their organizational functions, such as C-Level, Financial, Administrative, Etc.
Popularity
This report presents information about the incidence of e-mail addresses in other lists checked at SafetyMails, as shown in the table below:
- D1 – Rarely widespread: emails that are repeated rarely in other lists
- D2 – Not very widespread: emails that recur infrequently in other lists
- D3 – Widespread: emails that recur frequently in other lists
- D4 – Very widespread: emails that are repeated many times in other lists
This information serves to indicate that certain email addresses may be being heavily targeted by email marketing messages.




